Current Affairs Of Today Are
- 1) OPD registration system app
- 2) The DNA Technology (Use and Application) Regulation Act, 2019
- 3) India’s ‘longest’ river ropeway
- 4) DRDO identifies 108 Systems and Subsystems for the industry to design, develop and manufacture towards achieving “Atmanirbhar Bharat”
- 5) Government of India and AIIB sign agreement for $500 million
- 6) ARIES astronomers trace the mystery behind dwarf galaxy aberrations of massive star formation
- 7) INSPIRE faculty fellow developing low-cost biodiesel from microalgae
- 8) National Council for Transgender Persons
- 9) Atal Bimit Vyakti Kalyan Yojana: ESIC
- 10) BIS Draft Standard for Drinking Water
1) OPD registration system app
- Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal launched a mobile app and online OPD registration system for Shri Dada Dev Matri Avum Shishu Chikitsalaya. The app will be a convenient solution, especially for pregnant women during the time of the COVID-19 pandemic as they will no longer be required to stand in queues for registration.
- The Delhi government would launch the Hospital Management Information System (HMIS) to bring all hospitals in Delhi on one platform and then integrate the features of the app with HMIS to improve its efficiency.
- Shri Dada Dev Matri Avum Shishu Chikitsalaya conducts 10,000 deliveries across the year. This hospital has only 106 beds for now, but the capacity of the beds will be increased to 281 in the coming days, the inauguration of which was held in January this year and will be completed soon
- According to the Delhi government, the key features of the app include noqueue appointment, no waiting time, online Flu Clinic Registration for COVID-19, and helping prevent COVID19 infection by ensuring minimal contact with healthcare providers and other patients.
- The Delhi government is bringing together all hospitals in Delhi through the HMIS, including
- Mohalla Clinic, polyclinic, multispecialty, and super-specialty hospitals. This is a very ambitious project and will be completed within one year
Source: The Hindu
2) The DNA Technology (Use and Application) Regulation Act, 2019
- The Bill that proposes DNA sampling and profiling of citizens accused of a crime or reported missing and storing their unique genetic information for administrative purposes has some alarming provisions that could be misused for caste or community-based profiling, a draft report of the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Science and Technology has flagged.
- The committee, headed by Congress leader Jairam Ramesh but for want of quorum, the draft report, which has been circulated among the members, was not finalized.
- DNA Technology (Use and Application) Regulation Act, 2019, has been in the works for 15 years now. Nearly 60 countries have enacted similar legislation, with the U.S. bringing in law as far back as in 1994.
- The committee, in its draft report, pointed out that DNA profiles can reveal extremely
- sensitive information of an individual such as pedigree, skin color, behavior, illness, health status, and susceptibility to diseases.
- Under the provisions of the Bill, access to such intrusive information can be misused to specifically target individuals and their families with their own genetic data. This is particularly worrying as it could even be used to incorrectly link a particular caste/community to criminal activities
- The report also redflagged disregard for an individual’s privacy and other safeguards. The Bill proposes to store DNA profiles of suspects, undertrials, victims and their relatives for future investigations. While there is a good case for a DNA database of convicts, so that repeat offender may be easy identified, there is no legal or moral justification for a database with DNA of the other categories as noted above, given the high potential for misuse
- In the Bill, if a person is arrested for an offense that carries a punishment up to seven years, investigation authorities must take the person’s written consent before taking the DNA sample. But this consent is only “perfunctory”
- The Bill refers to consent in several provisions, but in each of those, a magistrate can easily override consent, thereby in effect, making consent perfunctory. There is also no guidance in the Bill on the grounds and reasons when the magistrate can override consent, which could become a fatal flaw
Source: The Hindu
3) India’s ‘longest’ river ropeway
- India’s ‘longest’ passenger ropeway across a river was unveiled in Guwahati almost a year after it was completed.
- The 1.82km bicable jig back ropeway connects a forested campus near the Kamrup (Metro) Deputy Commissioner’s office in the city on the southern bank of the Brahmaputra and a hillock behind the Doul Govinda temple in north Guwahati on the other.
- The ropeway passes over the midriver Peacock Island that houses Umananda, a medieval Shiva temple.
- The ₹56.08crore ropeway project was assigned to the Guwahati Metropolitan Development Authority
- (GMDA) in 2006. The foundation stone was laid in December 2009, a year after a Kolkata-based firm was awarded the construction work. A Swiss firm designed the cabins later
- The ropeway was scheduled to have been commissioned in May 2011 but an objection from the Archaeological Survey of India stopped the work in February that year. GMDA received permission to restart the project in 2015 on the condition that a pillar on a heritage island is realigned.
- The longest on land is the one in Gulmarg, Kashmir
- Each cabin could carry 32 people, including the operator, and the ride took about nine minutes one way
Source: The Hindu
4) DRDO identifies 108 Systems and Subsystems for the industry to design, develop and manufacture towards achieving “Atmanirbhar Bharat”
- Responding to the clarion call given by Hon’ble Prime Minister for “Atmanirbhar Bharat”, the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) has taken several initiatives to strengthen the indigenous defense ecosystem. Towards this, A DRDO delegation met with Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh today to apprise him about 108 systems and subsystems which have been identified for designing and development by the Indian Industry only. This initiative will pave the way for the Indian Defence industry to develop many technologies towards building an AtmaNirbhar Bharat.
- DRDO will also provide support to industries for the design, development, and testing of these systems on a requirement basis. All the requirements of these systems by R&D establishments, Armed Forces, and other Security Agencies can be met through development contracts or production orders on a suitable Indian industry. This will allow DRDO to focus on the design & development of critical and advanced technologies and systems.
- DRDO has been partnering with industry for the realization of its systems. Collaborating with DRDO in the development of major weapon systems the Indian industry has matured to a stage where they can develop systems on their own. Indian industry has progressed from a ‘build to print’ partner to ‘build to specification’ partner.
- The present industry base for DRDO consists of 1800 MSMEs along with DPSUs, Ordnance Factories, and large scale industries. DRDO has already taken major initiatives through various policies to involve the Indian industry as Development cum Production Partners (DcPP), offering its technology to industry at nominal cost and providing free access to its patents.
- This initiative will support the fast-growing Indian defense industrial ecosystem and will help the industry to contribute towards “Atmanirbhar Bharat” in a big way.
For a list of technology click here
Source: PIB
5) Government of India and AIIB sign agreement for $500 million
- The Government of India, the Government of Maharashtra, Mumbai Railway Vikas Corporation, and the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) signed a loan agreement for a $500 million Mumbai Urban Transport Project-III to improve the network capacity, service quality and safety of the suburban railway system in Mumbai.
- The Project is expected to increase network capacity in the region with a reduction in journey time and fatal accidents of commuters. It is estimated that among primary beneficiaries of the project, 22% are female passengers who will benefit from improved safety and quality of service.
- With a population of 22.8 million (2011), Mumbai Metropolitan Region (MMR) is the most populous metropolitan region in India and is expected to reach 29.3 million by 2031 and 32.1 million by 2041. This population growth represents the core driver behind Mumbai’s urban expansion, compelling the state of Maharashtra to prioritize sound urban and infrastructure planning which balances economic activities, mobility as well as the optimization of environmental and social outcomes.
- Around 86 percent of Mumbai commuters rely on public transport. However, supply has not kept pace with rising travel demand. The Mumbai suburban railway network, which carries three-quarters of all motorized travel (78 percent of passenger-km or eight million passengers per day) increasing at three percent annually, suffers from some of the most severe overcrowding in the world. User experience is further compromised by the low amenity of carriages, substandard stations and station access, and serious safety concerns. Between 2002-2012, there were more than 36,152 fatalities (on average, 9.9 fatalities per day) and 36,688 injuries on the Mumbai suburban railway network. A key reason for accidents and deaths is trespassing at or between stations as well as overcrowding of both stations and train cars.
- The total estimated cost of the project is $997 million, of which $500 million will be financed by the AIIB, $310 million by the Government of Maharashtra, and $187 million by the Ministry of Railways. The $500 million loans from the AIIB has a 5-year grace period and a maturity of 30 years.
Source: PIB
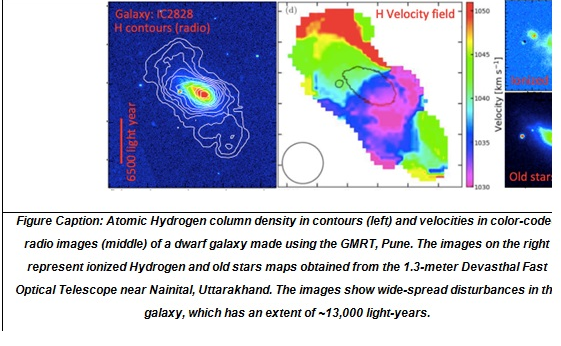
6) ARIES astronomers trace the mystery behind dwarf galaxy aberrations of massive star formation
Amidst the billions of galaxies in the universe, a large number are tiny ones 100 times less massive than our own Milky-way galaxy. While most of these tiny tots called dwarf galaxies form stars at a much slower rate than the massive ones, some dwarf galaxies are seen forming new stars at a mass-normalized rate 10-100 times more than that of the Milky-way galaxy. These activities, however, do not last longer than a few tens of million-years, a period which is much shorter than the age of these galaxies - typically a few billion years.
- Scientists observing dozens of such galaxies using two Indian telescopes have found that the clue to this strange behavior of these galaxies lies in the disturbing hydrogen distribution in these galaxies and also in recent collisions between two galaxies.
- To understand the nature of star formation in dwarf galaxies astronomers from Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES), an autonomous institute of Department of Science & Technology (DST), Govt. of India observed many such galaxies using the 1.3-meter Devasthal Fast Optical Telescope (DFOT) near Nainital and the Giant Meter wave Radio Telescope (GMRT). While the former operating at optical wavelengths sensitive to detect optical line radiation emanating from the ionized Hydrogen, in the latter 30 dishes of 45-meter diameter, each worked in tandem and produced sharp interferometric images via spectral line radiation at 1420.40 MHz coming from the neutral Hydrogen in galaxies.
- Star formation at a high rate requires a very high density of Hydrogen in the galaxies. According to the study conducted by the ARIES team, the 1420.40 MHz images of several intense star-forming dwarf galaxies indicated that hydrogen in these galaxies is very disturbed. While one expects a nearly symmetric distribution of hydrogen in well-defined orbits in galaxies, hydrogen in these dwarf galaxies is found to be irregular and sometimes not moving in well-defined orbits. Some hydrogen around these galaxies is also detected in forms of isolated clouds, plumes, and tails as if some other galaxy recently has collided or brushed away with these galaxies, and gas is scattered as debris around the galaxies. The optical morphologies sometimes revealed multiple nuclei and high concentration of ionized hydrogen in the central region. Although galaxy-galaxy collision was not directly detected, various signatures of it were revealed through radio, and optical imaging and these are helping to build up a story. The research, therefore, suggests that recent collisions between two galaxies trigger intense star formation in these galaxies.
- The findings of this research with detailed images of 13 galaxies will be appearing in the forthcoming issue of Monthly Notices of Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS) Journal published by the Royal Astronomical Society, the U.K. It will help astronomers to understand the formation of stars and evolution of less massive galaxies in the Universe.
Source: PIB
7) INSPIRE faculty fellow developing low-cost biodiesel from microalgae
- While fossil fuels deplete, the fuel potential of algae residing in the vast marine environment surrounding India remains unexplored. Low-cost biodiesel from microalgae of marine origin may soon turn a reality, thanks to the efforts of a scientist who is working on biotechnological studies and tools for increasing the lipid accumulation in microalgae for biodiesel production.
- Realizing the rapid depletion of petroleum-based fuels the National Institute of Technology, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, started exploring alternative fuels from renewable and sustainable sources. While different types of biofuels that have been explored recently, the use of microalgae has been strongly considered for the production of biofuels since they present a series of advantages over other biofuel feedstock, and this route to sustainable fuels inspired him.
- on techniques for enhancing Triacylglycerol content in marine microalgae towards economic biodiesel production received the "Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE) faculty fellowship instituted by the Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India.
- The team has isolated predominant strains of marine microalgal species namely Picochlorum sp., Scenedesmus sp., Chlorella sp., from the coastal regions of Tamil Nadu for their potential in terms of total organic carbon content, and Triacylglycerides(TAG) content for biodiesel production.
- They are now focusing on other microalgal candidates for their multiple biotechnological potentials and switchable polarity solvent (SPS) system based lipid extraction. SPS is an energy-efficient switchable solvent that can be recovered devoid of any thermal processes and can be reused as a green solvent for algal lipid extraction with no effect on the environment. Metabolic engineering approaches can be used to escalate TAG accumulation for increasing biodiesel yield, and magnetic nanocomposite (MNC) can be used for several cycles of algal dewatering, and its treated culture suspension can be reused to scale down the biodiesel production cost significantly. These three approaches would be considered in their study for sustainable and low-cost production of biodiesel.
- The group will formulate a roadmap by which biodiesel can be produced commercially and can be put in an energy market sustainably.
Source: PIB
8) National Council for Transgender Persons
- In exercise of the powers conferred by section 16 of the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 (40 of 2019), the Central Government has constituted a National Council for Transgender Persons vide notification dated 21st August 2020. The Union Minister of Social Justice & Empowerment will be Chairperson (ex-officio) and Union Minister of State for Social Justice & Empowerment will be Vice-Chairperson (ex-officio).
- The National Council shall perform the following functions, namely:—
- to advise the Central Government on the formulation of policies, programs, legislation and projects concerning transgender persons;
- to monitor and evaluate the impact of policies and programs designed for achieving equality and full participation of transgender persons;
- to review and coordinate the activities of all the departments of Government and other Governmental and non-Governmental Organisations which are dealing with matters relating to transgender persons;
- to redress the grievances of transgender persons; and
- to perform such other functions as may be prescribed by the Central Government.
- The other members of the Council include representatives of various Ministries/Departments, five representatives of the transgender community, representatives of NHRC and NCW, representatives of State Governments and UTs, and experts representing NGOs.
- A Member of National Council, other than ex officio member, shall hold office for a term of three years from the date of his nomination.
Source: PIB
9) Atal Bimit Vyakti Kalyan Yojana: ESIC
- The Employees' State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) has extended the Atal Bimit Vyakti Kalyan Yojana by one year to 30th June 2021.
- Further, the ESIC has relaxed eligibility criteria and enhanced the payment of the unemployment benefit under the Yojana (applicable from 24th March-31st December 2020).
About the Yojana:
- Atal Bimit Vyakti Kalyan Yojana was introduced w.e.f. 1st July 2018.
- Under it, the unemployment benefit is paid to the workers covered under the Employees' State Insurance (ESI) scheme.
- Unemployment benefit is paid in the form of cash compensation upto 90 days, once in a lifetime, to be claimed after three months (90 days) in one or more spells for being rendered unemployed.
- The employee should have completed two years of insurable employment and has contributed not less than 78 days in each of the four consecutive contribution periods immediately preceding to the claim of the relief.
- The benefit does not exceed 25% of the average earning per day.
About the ESI Act, 1948:
- It applies to all factories and notified establishments located in implemented areas employing 10 or more persons and applies to employees drawing wages up to Rs. 21,000 per month (Rs. 25,000 for persons with disabilities).
- In July 2019, the contribution rate under the ESI Act was reduced from 6.5% to 4% (employers’ contribution from 4.75% to 3.25% and employees’ contribution from 1.75% to 0.75%).
- In a financial year, there are two contribution periods each of six months duration.
- Employees in receipt of a daily average wage upto Rs.137 are exempted from payment of contribution.
- The Employees' State Insurance Scheme is administered by a corporate body called the ESI Corporation.
- The Corporation is the highest policy-making and decision making authority under the ESI Act and oversees the functioning of the Scheme.
- The Union Minister of Labour and Employment is its Chairman.
- It covers about 3.49 crore of family units of workers and provides cash benefits and medical facilities to 13.56 crore beneficiaries.
Source: PIB
10) BIS Draft Standard for Drinking Water
- Recently, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has prepared a draft standard for the supply system of piped drinking water.
- The draft has been titled as ‘Drinking water supply quality management system — requirements for piped drinking water supply service’.
Draft Standard:
- It outlines the process of water supply, from raw water sources to household taps.
- The draft standard is expected to make the process of piped water supply more uniform, especially in rural and underdeveloped areas of the country where the system runs on various government orders and circulars.
- The draft has been developed keeping in view the Centre’s Jal Jeevan Mission.
- The Jal Jeevan Mission aims for providing safe and adequate drinking water to all rural households by 2024 through tap connections.
- It has been prepared by the BIS’s Public Drinking Water Supply Services Sectional Committee.
Features of the Draft:
- It outlines the requirements for a water supplier or a water utility on how they should establish, operate, maintain, and improve their piped drinking water supply service.
- Guidelines for top management of the water supplier/utility which includes:
- Accountability and customer focus.
- Establishing a quality policy for their service.
- Monitoring the quality of water released to people.
- Conducting a water audit.
- It sets the Indian Standard (IS) 10500 for the treated water for drinking.
- The IS 10500 outlines the acceptable limit of heavy metals such as arsenic, pH value of water, turbidity, the total dissolved solids in it, and the color and odor.
- Adoption of the concept of the District Metering Area (DMA) where possible.
- DMA is a concept for controlling leakages in the water network, which is essentially divided into several sectors, called the DMAs, and where flow meters are installed to detect leaks.
- The water supplier may provide bulk water meters in the water distribution system to ensure water audit, however, the provisions should be made for domestic meters also.
- The water supplier shall ensure that the consumers do not have direct access to the meters to avoid possible tampering of the meters.
- The draft also mentions that water should be sampled at the treatment plant every four hours against quality parameters.
Background:
- Quality of drinking water became a contentious issue in November 2019 when a BIS report, released by Union Government, found Delhi’s tap water quality as the worst among 21 metros and state capitals in the country.
- The report had also found that tap water in 13 state capitals, including Bhopal, Chandigarh, Bengaluru, Kolkata, and Chennai, did not comply with BIS standards.
Jal Jeevan Mission
- Under this, the Union government envisages providing water supply to every household by 2024.
- The Mission is based on various water conservation efforts like point recharge, desilting of minor irrigation tanks, use of greywater for agriculture, and source sustainability.
- The Mission is based on a community approach to water and includes extensive Information, Education, and Communication as a key component of the mission.
- The Mission will converge with other Central and State Government Schemes to achieve its objectives of sustainable water supply management across the country.
- The Jal Shakti Ministry is the nodal ministry for the implementation of the mission.
Source: Indian Express


No comments:
Post a Comment